Certain body processes enable the organisms to live in their natural habitat. These body processes include respiration, digestion, excretion, etc. As the intake of the nutrients, the elimination of the waste from the body is a necessary process. The chief role of the human excretory system in the human body is the elimination of wastes produced by homeostasis. It is a specialized system that obtains, digests, and metabolizes nutrients in the body, which the excretory system further removes. During the process, the body sorts out the useful nutrients and exempts the unwanted matter, which is toxic and leaves the body as a residue. This process of waste removal is excretion. The mode of excretion differs from organism to organism, such as kidneys, lungs, skin, and eyes. In this guide, we’ll further discuss the different organs of the human excretory system and the mechanism associated with it.
Also read:-
Organs of a Kidney With Functions
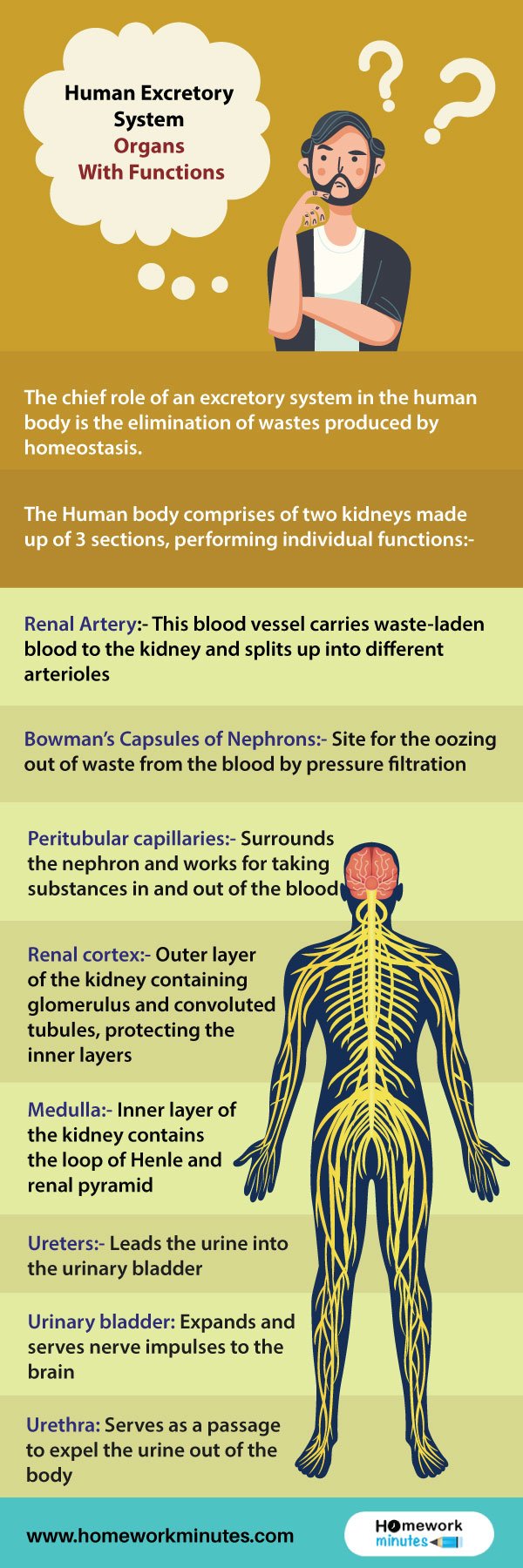
The Human body comprises of two kidneys made up of 3 sections, performing individual functions:-
Renal Artery
This blood vessel carries waste-laden blood to the kidney and splits up into different arterioles
Bowman’s Capsules of Nephrons
Site for the oozing out of waste from the blood by pressure filtration
Peritubular Capillaries
This part of the human excretory system surrounds the nephron and works for taking substances in and out of the blood
Renal cortex
The outer layer of the kidney containing glomerulus and convoluted tubules, protecting the inner layers
Medulla
The inner layer of the kidney contains the loop of Henle and renal pyramid
Renal pelvis
Takes urine away from the kidney via the ureter
Ureters
This part of the human excretory system leads the urine into the urinary bladder
Urinary bladder
Expands and serves nerve impulses to the brain
Urethra
This part of the human excretory system serves as a passage to expel the urine out of the body
Also read:-
Mechanism of Excretion in Humans
Excretion is the process of the removal of metabolic wastes from the body. In the human body, the different life processes take place simultaneously like respiration, circulation, digestion, etc. The main waste products in the human body include carbon dioxide, water, and nitrogenous products like urea, ammonia, and uric acid. The removal of these chemicals and toxic compounds takes place in a series of processes.
To initiate the main processes, the key organ is a kidney. The kidney is the main excretory organ of the human body that helps the body to separate the useful substances by reabsorption and toxic substances by converting it into the urine. For the kidney to filter toxic substances, it contains a million nephrons. More so, the kidney contains capillaries that filter the blood and contains essential substances like glucose, amino acids, etc. After that, the pureblood then circulates into the other body parts.
The human body contains an excess of water and nitrogenous waste. In the process of excretion, the produced urine passes the urinary bladder via the ureters. The central nervous system controls the urinary bladder and signals it to contract and then excrete the urine through a passage called the urethra.
If you need any help with any such biology topics, you can get instant online assignment help from the top-experts at Homework Minutes. We’re available to provide you 24*7 help instantly.